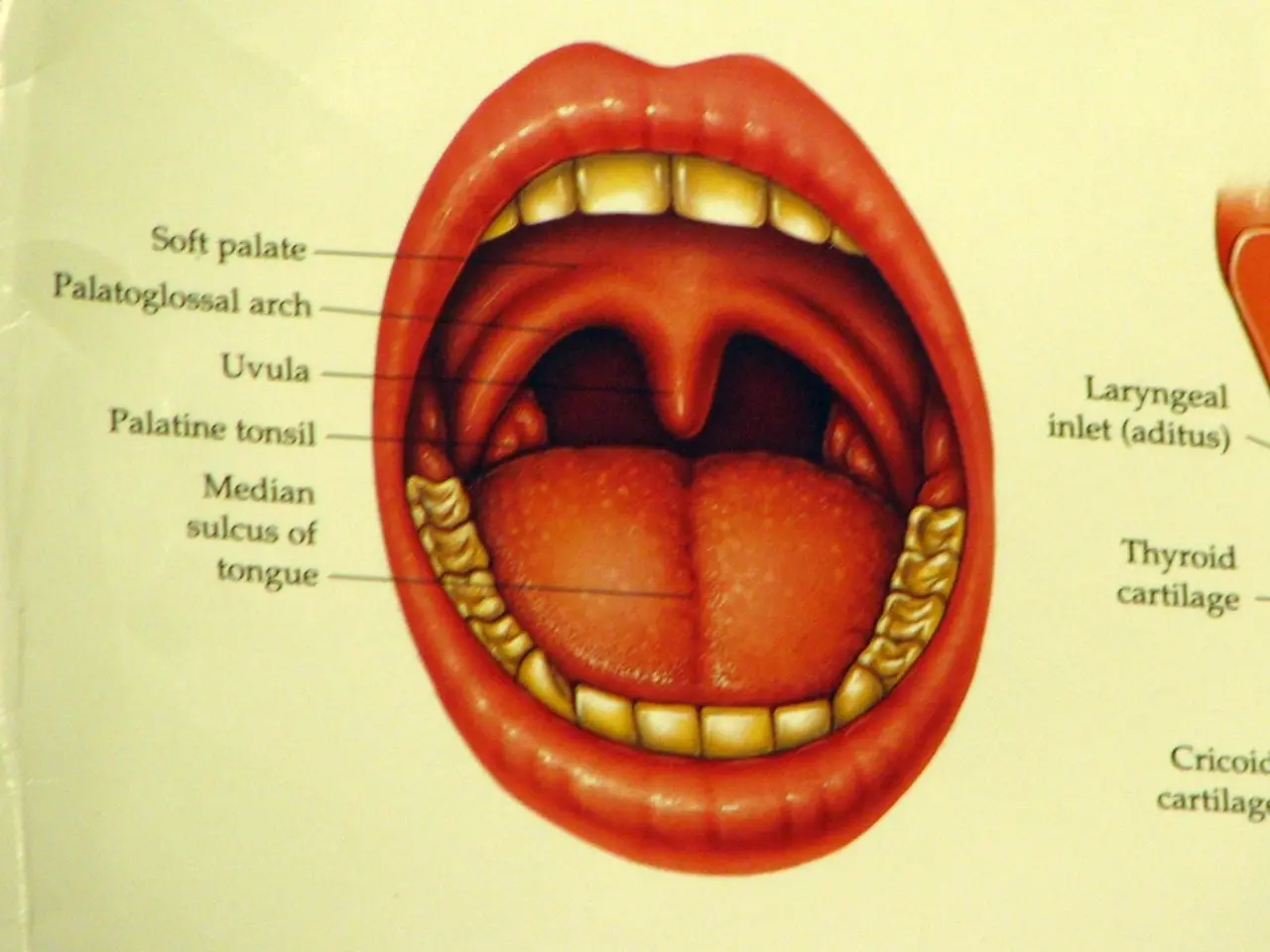
Surgical excision of the tongue: What steps does this operation encompass?
In the realm of medical procedures, a glossectomy stands as a significant operation that involves the removal of a part or all of the tongue. This surgical procedure is often recommended for malignant or premalignant tongue tumors.
Specialists who perform glossectomies are typically otolaryngologists (ENT surgeons) or head and neck surgeons. Their expertise ensures the best possible outcome for patients.
The extent of the surgery depends on the size and stage of the tumor. For smaller tumors, a partial glossectomy might suffice, with the affected area healing on its own or requiring minor reconstruction. However, for more extensive tumors, a subtotal or total glossectomy may be necessary. In such cases, reconstruction becomes crucial to optimize the person's ability to swallow and speak.
Transcervical pull-through and lip-split mandibulotomy are two approaches surgeons might use. Transcervical pull-through involves creating an opening in the neck to reach the tongue area and perform reconstruction on the soft tissue. On the other hand, lip-split mandibulotomy involves removing a part or all of the lower jaw bone and making an incision through the lips to expose the tongue, possibly requiring reconstruction with flaps and bone grafts.
Imaging techniques such as flexible laryngoscopy help assess whether a tumor has extended to areas beyond the tongue. Determining the extent of the tumor and creating an airway plan beforehand is crucial to ensure a smooth operation.
Following a glossectomy, a person may have a breathing tube in their neck or nasal cavity, tubes for feeding and fluid drainage. Recovery can be challenging, with some individuals experiencing difficulty speaking and swallowing, requiring rehabilitation or further procedures. Speech and voice therapy can help people improve their speaking ability after a glossectomy.
It's important to note that a glossectomy can permanently alter a person's speech. In some cases, a person may not be able to eat for a few days after the surgery.
While glossectomy can be an effective treatment option for conditions like macroglossia and obstructive sleep apnea, it is not without risks and complications. These include bleeding, pain, swelling, damage to nearby structures, drooling, difficulty swallowing, difficulty chewing, difficulty speaking, changes in tongue sensation, changes to the appearance of the lips, oral fistulae, nonhealing wounds, scarring, lymphedema, nerve damage, weight loss, anesthesia-related complications, and more.
Before the procedure, doctors will perform examinations and tests to determine a person's fitness for surgery. This includes a physical examination, complete blood count, heart and lung function tests, blood clotting and liver function tests, a nutritional assessment, a dental exam, and an assessment of the clinical history and past treatment.
After undergoing a glossectomy, a person should contact a doctor if they experience side effects such as fever and chills, increased swelling, difficulty swallowing, nausea and vomiting, choking, severe pain, excessive bleeding, or signs of infection.
In conclusion, a glossectomy is a complex surgical procedure with potential life-changing implications. However, with the expertise of specialized surgeons and proper pre and post-operative care, many patients can successfully overcome their tongue tumors and return to a quality life.